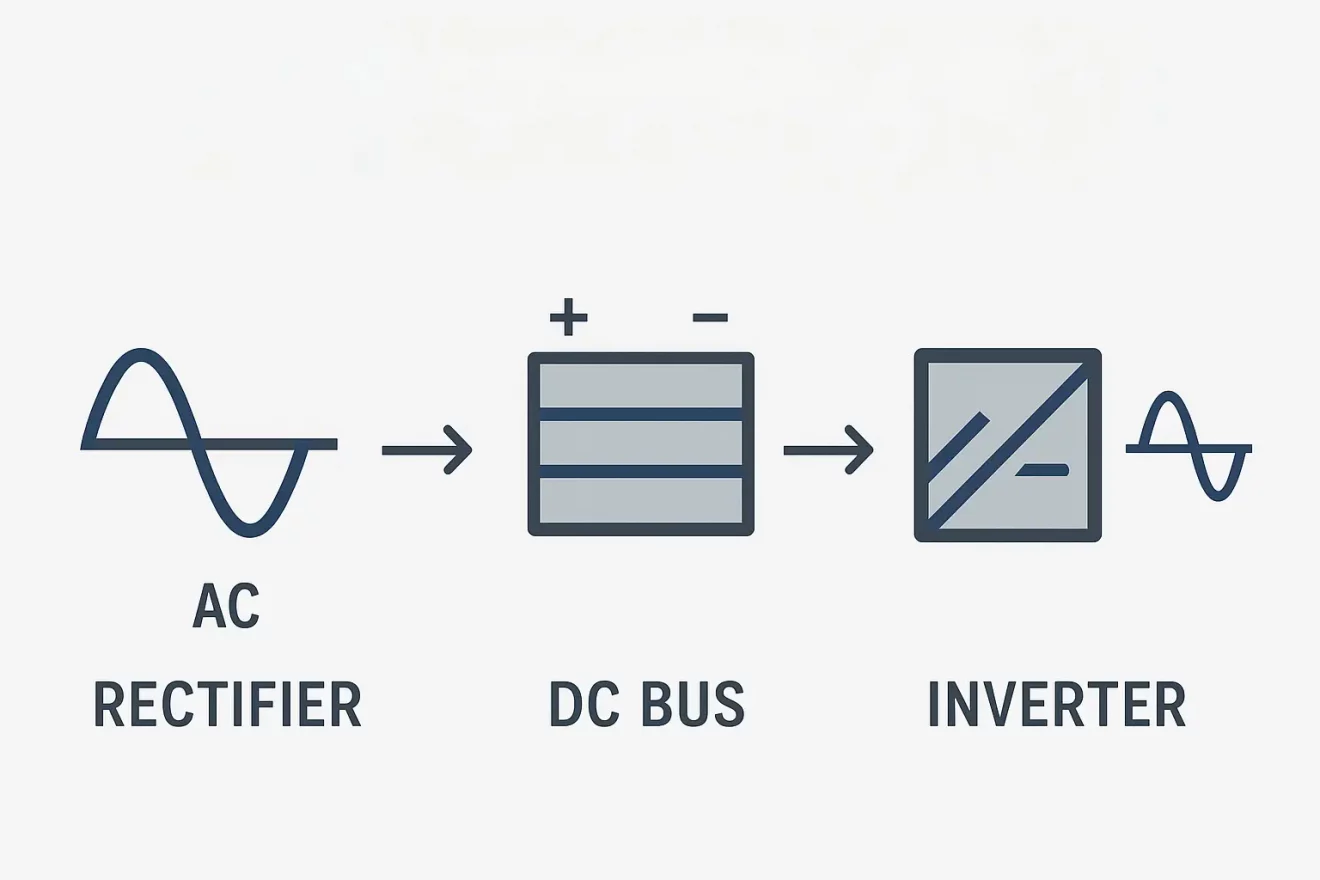
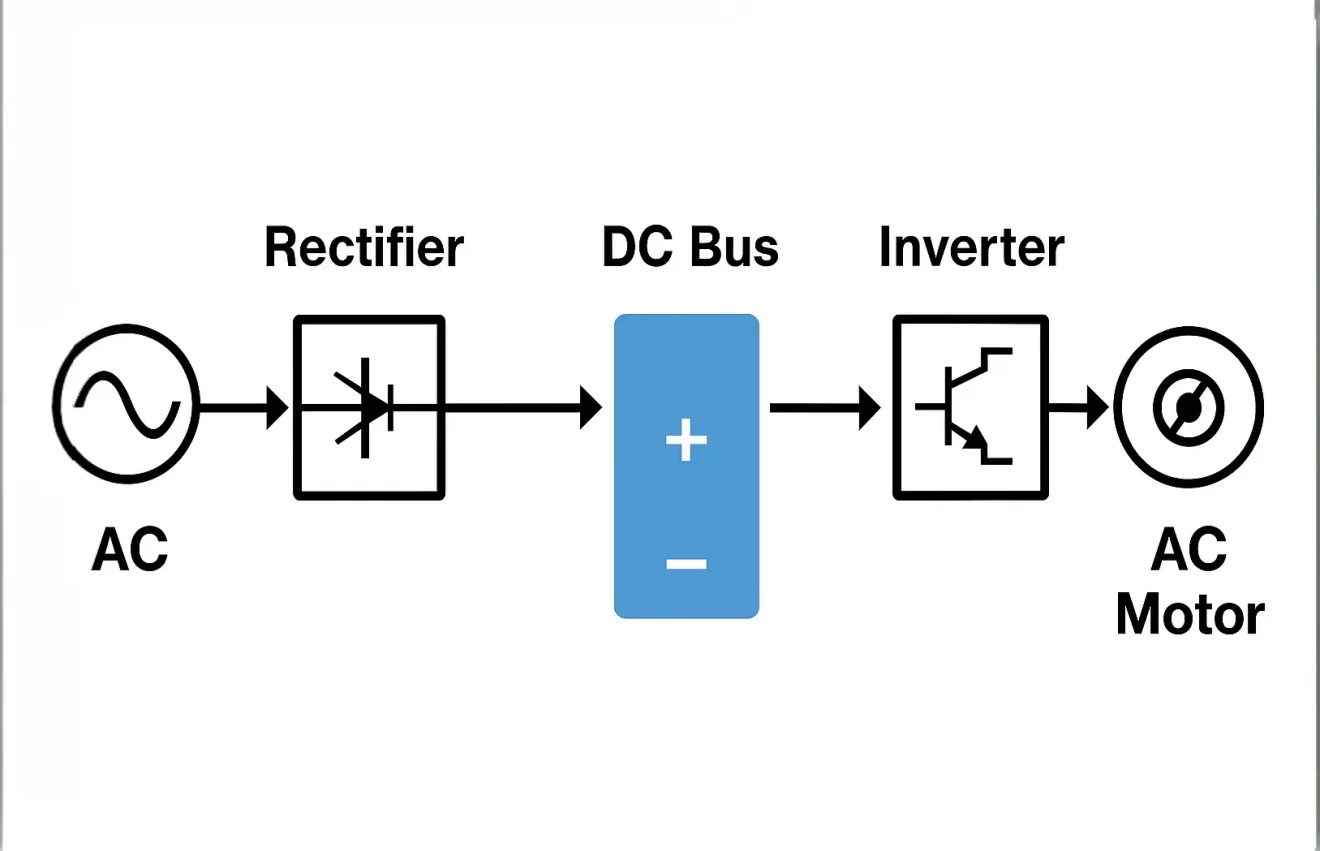
When motor control lacks precision, energy is wasted, equipment fails early, and production efficiency drops sharply — Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) provide the solution.
A Variable Frequency Drive (VFD), also known as a frequency inverter or Variable Speed Drive (VSD), converts AC to DC and back to controlled AC power to regulate motor speed and torque efficiently. It’s a core technology bridging alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) systems.
Curious how AC and DC interact inside a VFD? Let’s explore how these two forms of power work together to make modern automation possible.
What Defines a VFD?
A Variable Frequency Drive (VFD)—sometimes called a Variable Speed Drive (VSD) or frequency inverter—is an intelligent control device that regulates the speed, torque, and direction of an electric motor. By changing the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor, a VFD ensures optimal operation, energy efficiency, and equipment longevity.
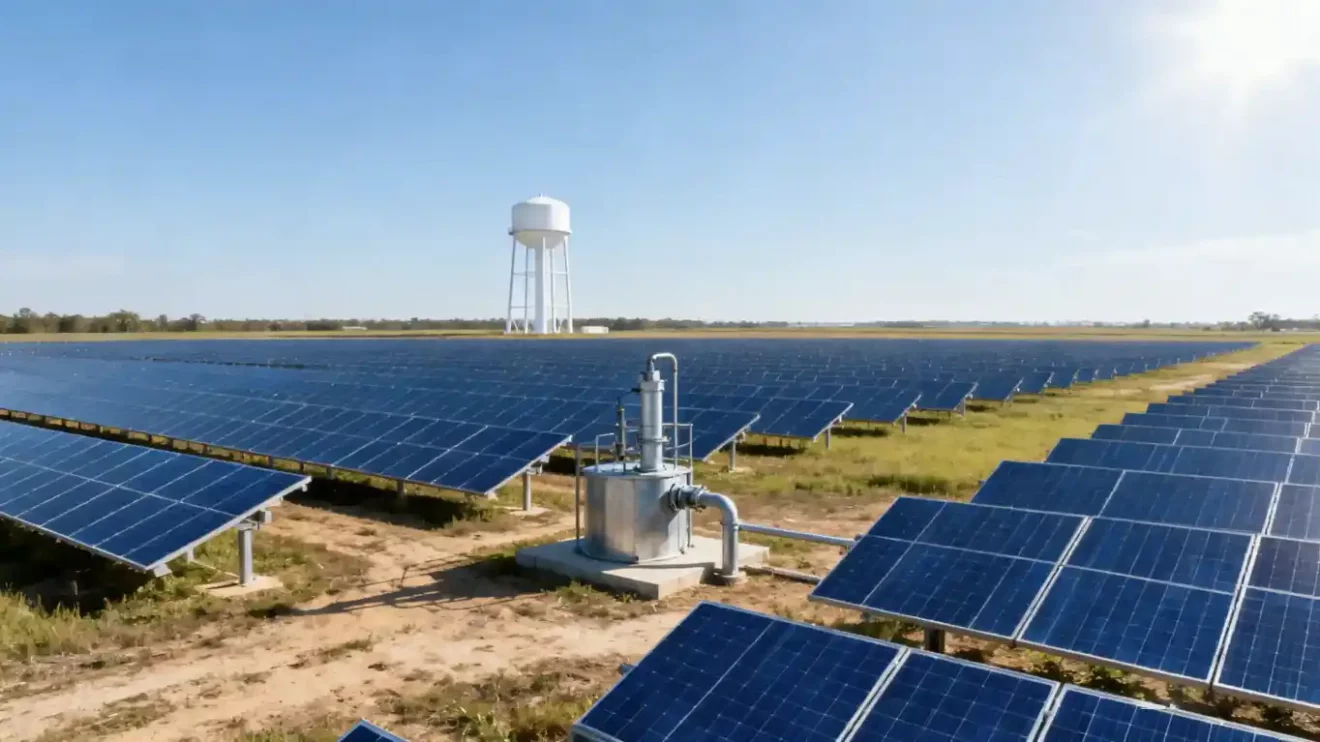
In industrial automation and renewable energy systems, VFDs have become indispensable. They reduce mechanical stress, save energy, and allow for precise control of processes ranging from water pumping to conveyor systems. As a leading VFD manufacturer in China, USFULL focuses on producing reliable and customizable VFDs for global clients who demand performance and stability in every application.
How Does a VFD Work?
A VFD operates through three main stages: rectification, DC bus storage, and inversion. First, it rectifies incoming AC power into DC using a diode bridge. This DC power is then stored and smoothed in the DC bus capacitors to maintain stable voltage. Finally, the inverter section—using IGBTs (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors)—converts the DC back into variable-frequency AC, controlling motor speed precisely.
This continuous conversion enables a VFD or variable frequency inverter to adjust motor output without mechanical gears or throttling, achieving both energy savings and fine speed control. It’s the reason why frequency inverters are widely used in factories, HVAC systems, and solar-powered equipment.
What’s the Role of AC and DC in VFDs?
The interplay of AC and DC within a VFD is central to its function. While the input and output are AC, the intermediate process operates on DC. The incoming AC power is first rectified into DC, forming a smooth and stable energy bank in the DC bus. Then, the inverter converts this DC back into AC with adjustable frequency and amplitude.
This dual conversion process allows VFDs to control induction motors with remarkable precision. The AC stage provides compatibility with the grid and motors, while the DC stage ensures stable power transformation. This integration of AC and DC technologies is what makes the inverter VFD such a powerful and flexible control device.
Are There DC VFDs?
Although VFDs are generally designed for AC motors, there are specialized models known as DC VFDs or DC variable speed drives. These units are used in systems powered directly by DC sources such as batteries or solar panels, or in legacy applications that rely on DC motors.
However, DC VFDs are less common today because AC VFD systems offer greater efficiency, lower maintenance, and broader availability. Modern industries increasingly adopt AC inverter VFDs, which are easier to integrate with renewable energy systems and global AC standards. As a professional VFD supplier, USFULL focuses primarily on high-performance AC VFDs while supporting hybrid solutions for DC systems when required.
Why Prefer AC VFDs Over DC Drives?
AC VFDs dominate modern automation because they are cost-effective, reliable, and energy-efficient. Compared to traditional DC drives, AC VFDs require less maintenance, have longer lifespans, and are compatible with standard power grids.
Furthermore, AC induction motors—which pair perfectly with VFDs—are simpler, more robust, and more affordable than DC motors. This makes AC variable frequency drives ideal for industries ranging from manufacturing to agriculture. Leading VFD manufacturers, like USFULL, continue to innovate AC drive technology to provide enhanced control accuracy and power efficiency.
What Are the Applications of VFDs?
The versatility of variable frequency drives makes them integral to countless industries. Common applications include:
Solar pumping systems using MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) control
HVAC and ventilation systems to regulate airflow and reduce energy waste
Industrial conveyors and mixers for speed adjustment and process optimization
Water treatment and irrigation for precise pump control
At USFULL, a trusted VFD manufacturer in China, our products are widely used across more than 90 countries, ensuring reliable operation and efficiency in both industrial and agricultural sectors.
How Do You Choose the Right VFD for Your Application?
Choosing the right VFD or frequency inverter depends on several key factors: motor type, rated power, voltage level, control mode, and environmental conditions. It’s also important to consider protection features like overcurrent, overvoltage, and thermal control.
A professional VFD manufacturer will provide expert guidance to match your specific application—whether it’s for a solar pump inverter, HVAC fan, or industrial automation system. USFULL offers tailored recommendations and custom branding options, ensuring you get a reliable, cost-effective variable frequency inverter that fits your operational needs.
What is a VFD DC Bus?
The DC bus is the intermediate energy storage circuit within a VFD. After AC power is rectified, it becomes DC and is stored in capacitors connected across the DC bus. This section stabilizes voltage, filters noise, and prepares power for reconversion into AC by the inverter stage.
Without the DC bus, the VFD couldn’t provide smooth, adjustable frequency control. In essence, it acts as the energy reservoir that ensures steady, efficient power delivery to the motor.
What is the Use of DC Bus Voltage in VFD?
The DC bus voltage in a Variable Frequency Drive plays a critical role. It:
Stores converted energy from AC to DC.
Smooths voltage fluctuations for stable inverter operation.
Supplies energy to the IGBT inverter stage for motor control.
By maintaining consistent DC bus voltage, a VFD can precisely regulate motor speed and torque. This ensures optimal performance, especially in energy-sensitive systems such as solar pump inverters and industrial automation drives.
What is an IGBT in a VFD?
An IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) is the electronic heart of an inverter VFD. It acts as a high-speed switch that converts DC bus voltage into variable-frequency AC power. By turning on and off thousands of times per second, IGBTs create a synthesized AC waveform that controls the motor’s speed and torque.
This advanced semiconductor technology allows VFD manufacturers to deliver compact, efficient, and precise control systems. IGBTs combine the high current handling of bipolar transistors with the fast switching capability of MOSFETs—ensuring durability and minimal energy loss.
What is MPPT VFD?
An MPPT VFD (Maximum Power Point Tracking Variable Frequency Drive) is specifically designed for solar applications. It continuously tracks the optimal operating point of solar panels to extract maximum power, then uses that energy to drive motors—commonly for solar water pumping systems.
By combining MPPT technology with variable frequency control, the solar VFD maximizes energy utilization, ensuring consistent water output even under fluctuating sunlight. As a professional VFD supplier and solar inverter manufacturer, USFULL offers advanced MPPT VFDs that provide reliable, energy-efficient performance for off-grid and agricultural operations.
In summary, VFDs are AC-based control devices that internally utilize DC conversion to achieve precision, efficiency, and flexibility in motor control. As a trusted VFD manufacturer in China, USFULL continues to develop advanced variable frequency drives, solar pump inverters, and variable frequency inverter solutions that empower industries worldwide toward smarter, greener operations.