Electrical faults can cause fires, equipment damage, or fatal accidents—choosing the wrong protection device makes risks worse. Reliable RCCB, RCBO, and RCD solutions prevent disasters.
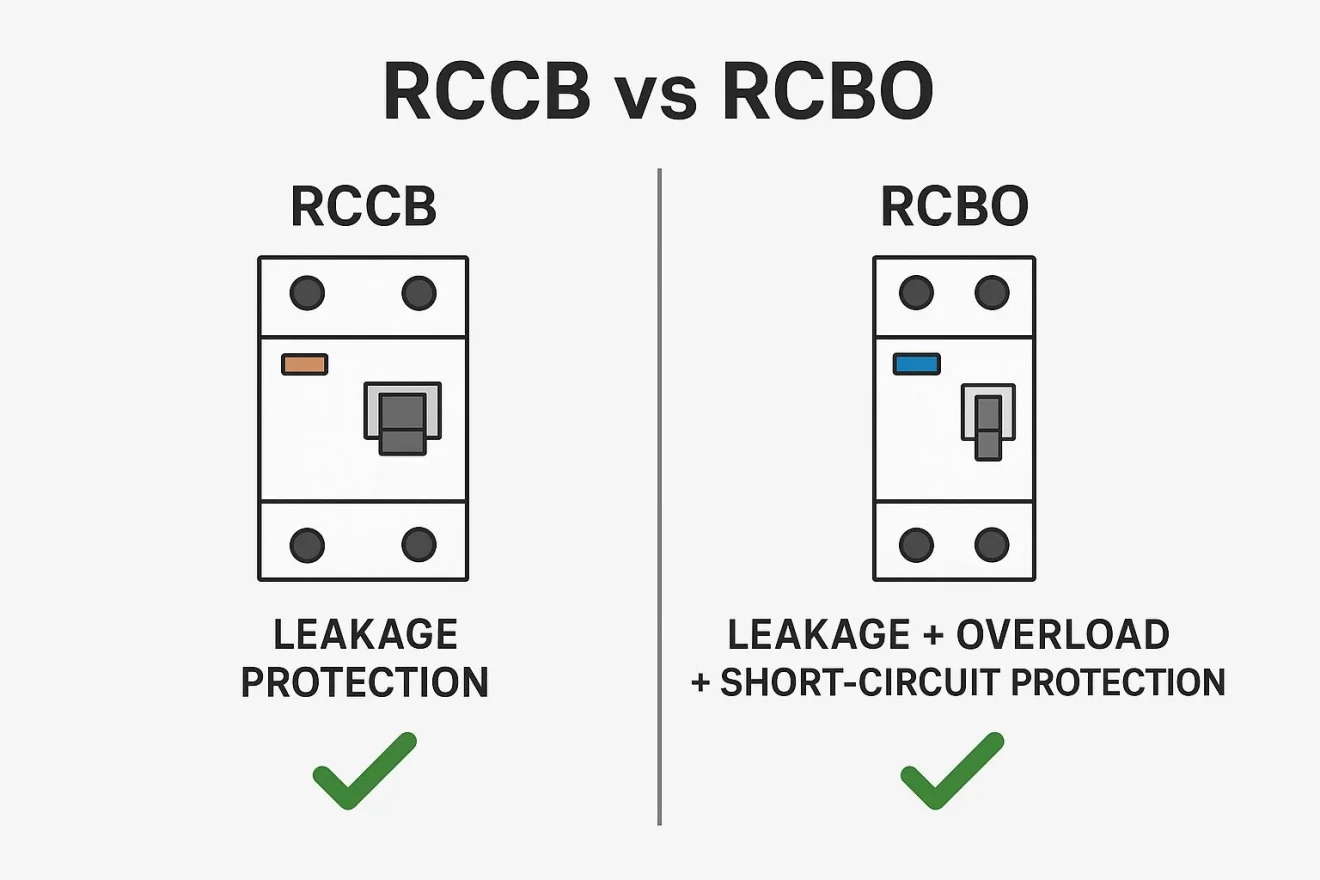
RCCB, RCBO, and RCD are essential electrical safety devices. An RCCB only protects against residual current (leakage), while an RCBO integrates residual current and overcurrent protection. RCD is the general term covering both devices.
Keep reading to understand the differences between RCCB, RCBO, and RCD.
What Is an RCCB?
Eine RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker) is a protective device designed to detect leakage current, also called residual current, in an electrical circuit. When current flows through an unintended path—such as through a person to earth—the RCCB immediately disconnects the power supply, preventing electric shock and reducing fire hazards.
The key feature of an RCCB is that it does not provide overcurrent protection. It is purely a leakage protection device. For this reason, RCCBs are often installed together with MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers) oder MCCBs (Molded Case Circuit Breakers) to provide complete circuit protection.
RCCBs are widely used in homes, offices, and industrial facilities. A typical household RCCB is set to trip at 30mA, the level considered safe for human protection. Higher trip settings, such as 100mA or 300mA, are often used in industrial applications for fire prevention.
Als vertrauenswürdiger RCCB manufacturer in China, USFULL provides RCCBs that comply with IEC and GB/T standards, ensuring reliable safety performance in both residential and commercial installations.
What Is an RCBO?
Eine RCBO (Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent protection) combines the functions of an RCCB and an MCB in a single device. This means it protects against residual current (leakage), overload, and short circuit.
The advantage of an RCBO is its all-in-one design. Instead of installing separate RCCBs and MCBs, one RCBO ensures both leakage and overcurrent protection. This not only saves panel space but also simplifies wiring, making it ideal for modern installations where space is limited.
RCBOs are especially useful in commercial and industrial projects where equipment is sensitive and downtime is costly. By providing comprehensive protection, RCBOs reduce the risk of electrical accidents, equipment failure, and fire hazards.
What Is an RCD?
Eine RCD (Residual Current Device) is a broad category of devices that detect residual current and disconnect circuits when leakage exceeds safe levels. RCCBs and RCBOs are both types of RCDs, but the term also covers leakage relays, contactors with residual protection, and socket-type devices such as GFCIs in the United States.
In essence, RCD is the umbrella term. Zum Beispiel:
RCCB = RCD that provides leakage protection only.
RCBO = RCD that provides leakage + overcurrent protection.
MCCB with leakage module = RCD combined with molded case breaker.
International standards such as IEC 60755, IEC 61008, and IEC 61009 define the requirements for RCDs. When sourcing from an RCCB manufacturer in China, confirming compliance with these standards ensures product reliability.
What Is the Difference Between RCCB and RCBO?
Die main difference between RCCB and RCBO lies in whether the device provides overcurrent protection:
RCCB: Detects and interrupts leakage only. Requires an MCB or MCCB to handle overloads and short circuits.
RCBO: Provides both leakage protection and overcurrent protection in a single device.
Choosing between them depends on the application:
For residential use, RCCBs combined with MCBs are cost-effective.
For industrial or commercial use, RCBOs save panel space and simplify wiring, making them the preferred option.
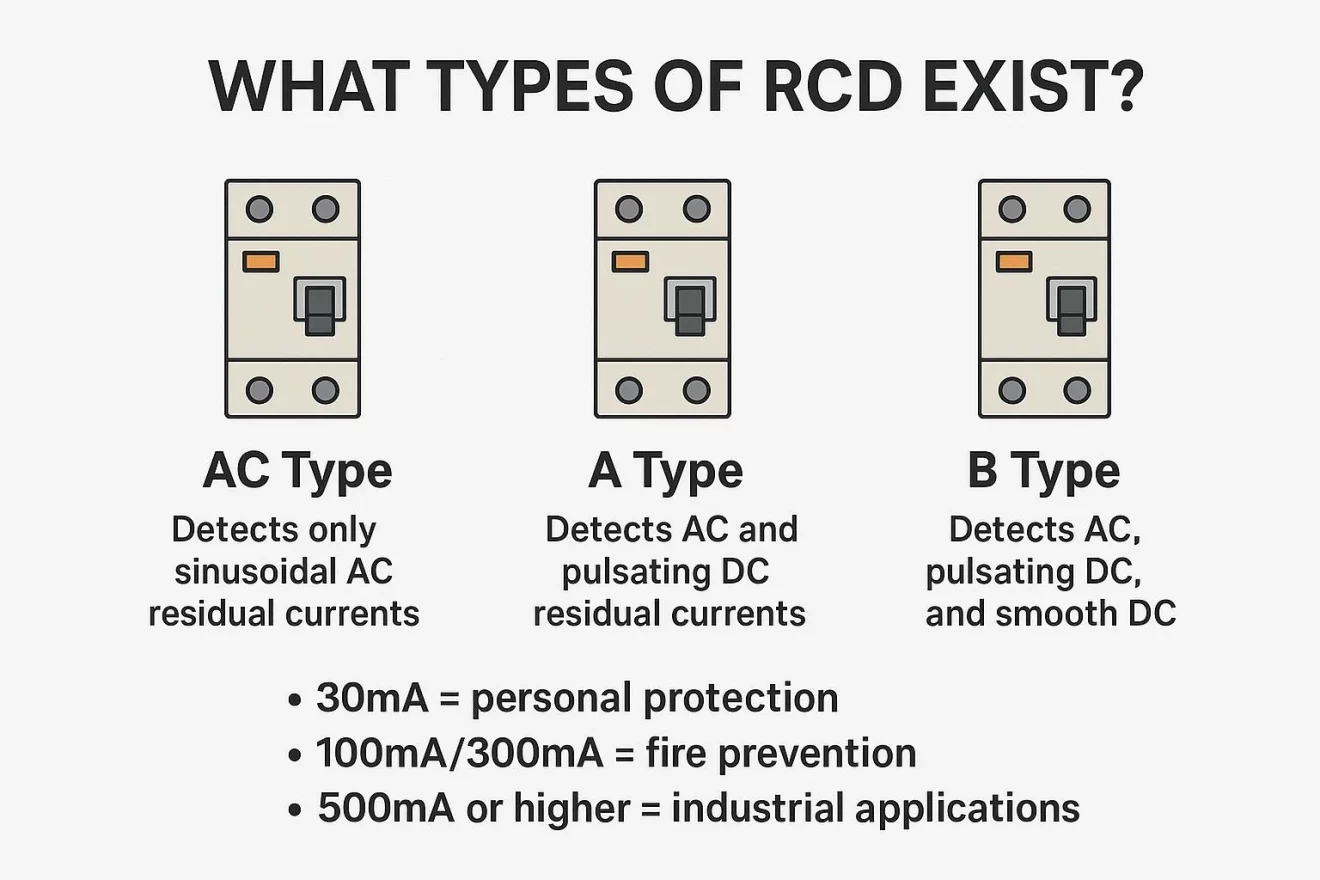
What Types of RCD Exist?
RCDs come in several sensitivity types, each suitable for different applications:
AC Type: Detects only sinusoidal AC residual currents.
A Type: Detects AC and pulsating DC residual currents.
B Type: Detects AC, pulsating DC, and smooth DC, suitable for variable frequency drives, photovoltaic systems, and EV charging stations.
In addition, RCDs are rated by tripping current and response time.
30mA = personal protection.
100mA/300mA = fire prevention.
500mA or higher = industrial applications.
What Are Common Mistakes When Using RCCB, RCBO, or RCD?
Even when sourcing from a reliable RCCB manufacturer, installation and usage mistakes can reduce protection effectiveness. Common issues include:
Assuming RCCBs protect against overcurrent – they only protect against leakage.
Incorrect wiring – all live conductors and neutral must pass through the RCCB/RCBO’s sensing core.
Ignoring the test button – standards recommend pressing the “TEST” button regularly to verify performance.
Blaming devices for nuisance tripping – sometimes caused by long cable capacitance, filters, or faulty equipment rather than the breaker itself.
Proper training, correct device selection, and cooperation with professional suppliers ensure RCCBs, RCBOs, and RCDs perform as intended.