Unexpected VFD malfunctions, overvoltage, or motor failures often occur due to improper cable selection—choosing the right cable solves it.
Shielded cables include a conductive layer that reduces electromagnetic interference, while unshielded cables lack this protection, offering lower capacitance and better voltage stability for VFD системы.
Keep reading to learn how to choose the right cable for your VFD system.
What Is a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) and Why Cable Selection Matters?
A Variable Frequency Drive (VFD), also known as a variable frequency inverter, inverter VFD, or Variable Speed Drive (VSD), controls the speed and torque of AC motors by varying frequency and voltage. In industrial applications, VFDs improve energy efficiency, reduce mechanical stress, and enable process automation.
Cable selection is crucial because the connection between the VFD and motor carries high-frequency switching signals that generate electromagnetic interference (EMI). Using the wrong cable—shielded or unshielded—can lead to voltage reflections, motor insulation stress, and frequency inverter malfunctions. A VFD manufacturer in China or a global VFD supplier will always recommend proper cable types to ensure stable and safe operation.
What Are Shielded Cables and Their Benefits for VFD Systems?
Shielded cables feature an additional metallic layer, often copper braid or aluminum foil, surrounding the conductors. This shielding layer blocks or absorbs electromagnetic interference emitted by the variable frequency drive, preventing it from affecting nearby sensitive equipment.
Benefits of shielded cables for frequency inverters include:
EMI protection: Reduces interference with control circuits and communication networks.
Safety in dense installations: Ideal for factories with multiple Variable Speed Drives.
Compliance with standards: Many industrial sites require shielded cables for regulatory reasons.
However, shielded cables also increase distributed capacitance, which can raise motor terminal voltage and generate current spikes, occasionally triggering VFD overcurrent trips. That is why leading VFD manufacturers in China often advise adding output filters or reactors when using shielded cables on long runs.
What Are Unshielded Cables and When Should They Be Used?
Unshielded cables, sometimes called U-TP motor cables, contain only insulated conductors without a metallic shield. They are simpler, lighter, and more cost-effective than shielded cables.
Key advantages in VFD applications include:
Lower distributed capacitance: This reduces the risk of high voltage reflections at the motor terminals.
Better voltage stability: Unshielded cables are less likely to cause inverter overvoltage errors.
Easier installation: Flexible and lighter, suitable for short-distance wiring in low-EMI environments.
However, unshielded cables provide no EMI suppression. In plants with multiple frequency inverters or sensitive automation systems, unshielded wiring may lead to interference with sensors, PLCs, or communication lines. Leading VFD suppliers typically recommend unshielded cables only for short motor leads in low-interference applications.
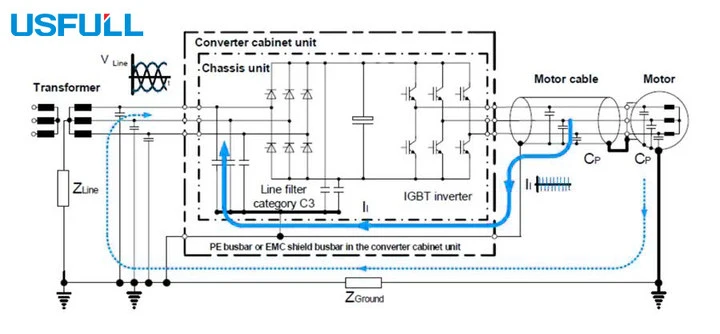
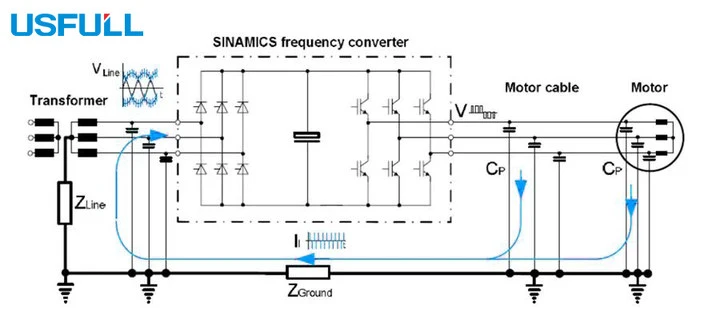
How Does Cable Capacitance Affect VFD Performance?
Distributed capacitance is the hidden factor that determines how shielded or unshielded cables influence инверторный ЧРП performance. Capacitance occurs naturally between the motor cable conductors and ground, and shielded cables increase this capacitance because of the additional metallic layer.
High cable capacitance can:
Raise reflected voltage peaks at the motor terminals.
Increase current spikes, sometimes triggering VFD overcurrent faults (e.g., Err02 or Err03 or Err04).
Accelerate motor insulation wear, reducing the lifespan of the motor and frequency inverter.
To manage capacitance-related issues, variable frequency drive manufacturers suggest using shorter cables, output reactors, or dV/dt filters. This is especially important when using shielded cables with long motor runs in industrial Variable Speed Drive applications.
Which Cable Should You Choose for Your VFD System?
The decision between shielded and unshielded cables depends on your operating environment and application requirements:
Use Shielded Cables if:
Your installation has multiple VFDs or sensitive electronics.
Compliance with EMI regulations is mandatory.
The motor cable length is moderate (shorter than 50m recommended without extra filtering).
Use Unshielded Cables if:
The motor lead is short and EMI risk is low.
Voltage stability is more critical than interference protection.
You want cost-effective wiring with easier installation.
В качестве professional VFD manufacturer and supplier, USFULL advises customers to evaluate cable length, interference risk, and motor insulation class before making a choice. A variable frequency drive manufacturer in China can also provide custom solutions with filters to optimize performance for either cable type.