Inefficient motor speed control wastes energy, causes mechanical stress, and shortens equipment lifespan — a VFD solves this by adjusting motor speed smoothly and precisely.
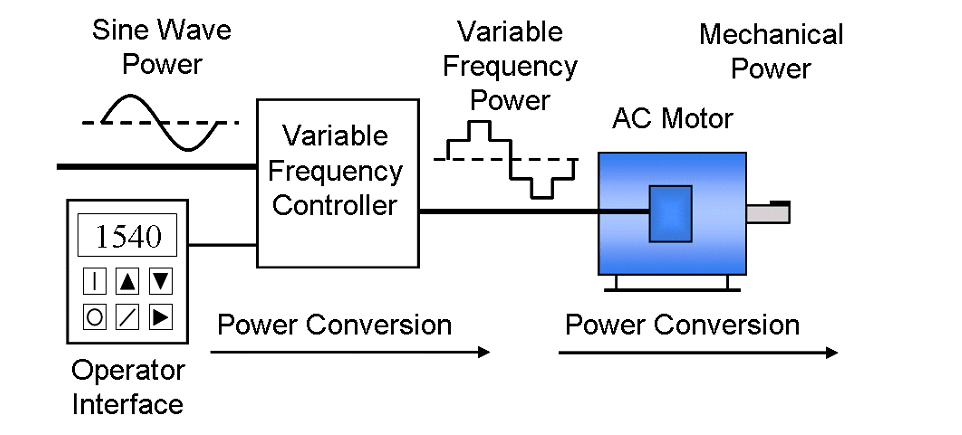
A Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) slows down a motor by reducing the frequency and voltage of the power supplied to it. It does this by converting AC to DC, and then back to AC with controlled frequency using Pulse Width Modulation (PWM).
Discover how this powerful solution optimizes energy use and protects your equipment.
What is a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD)?
A Variable Frequency Drive (VFD), also known as a frequency inverter, variable speed drive (VSD), or variable frequency inverter, is a type of motor controller that regulates the speed and torque of an electric motor by adjusting the frequency and voltage of the power it receives.
In industrial applications, motors often run at full speed even when the load requires less power. A VFD solves this inefficiency by controlling motor speed based on real-time demand. This not only improves energy efficiency but also reduces mechanical wear and extends equipment life.
How Does a VFD Work Internally to Control Speed?
A variable frequency drive works through three main stages:
Rectification: The incoming AC power is converted to DC using a rectifier circuit.
Filtering: The DC power is smoothed by capacitors.
Inversion: The DC is then converted back to AC using IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) switches. These switches simulate an AC waveform with adjustable voltage and frequency using Pulse Width Modulation (PWM).
By controlling both the frequency and voltage of the output power, the inverter VFD controls how fast the motor’s magnetic field rotates, effectively slowing down or speeding up the motor as needed.
Why Does Frequency Affect Motor Speed?
The speed of an AC motor is directly related to the frequency of the electrical supply. Specifically, motor speed in RPM (revolutions per minute) is determined by the formula:
RPM = (120 × Frequency) / Number of Poles
When a VFD lowers the output frequency, the rotating magnetic field inside the motor slows down, causing the motor shaft to turn more slowly.
For example, a motor rated for 50 Hz will spin at a certain speed. If the VFD reduces the frequency to 30 Hz, the motor will run at only 60% of its rated speed — saving energy and reducing mechanical strain.
As a leading VFD supplier, USFULL ensures that our products deliver accurate and stable frequency control for demanding applications.
What is Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) and Why Does It Matter?
PWM is a key function of every quality frequency inverter. It involves rapidly switching the DC voltage on and off in pulses to mimic a sinusoidal AC waveform. By changing the width and frequency of these pulses, the VFD controls both:
The voltage delivered to the motor
The frequency of the waveform
This results in a highly efficient and smooth simulation of AC power, allowing the motor to operate at variable speeds with minimal vibration and noise.
PWM also contributes to energy savings and reduces heat buildup, making VFDs ideal for solar pumping, ventilation systems, and industrial automation.

What Are the Advantages of Slowing Down a Motor with a VFD?
Using a variable frequency inverter to slow down a motor offers many performance and cost-saving benefits:
Energy Efficiency: VFDs adjust motor output to match demand, cutting energy use by up to 50% in some cases.
Reduced Mechanical Stress: Gradual acceleration/deceleration extends equipment lifespan.
Lower Maintenance Costs: Smoother starts and stops prevent mechanical wear and tear.
Noise Reduction: Slower speeds lead to quieter operation, especially in fans and pumps.
System Protection: Built-in overload, overvoltage, and short-circuit protection keep motors safe.
These advantages make the inverter VFD a must-have for industries looking to increase reliability and reduce operational expenses.
Where Are VFDs Commonly Used?
Variable speed drives are used across multiple industries due to their versatility:
Water Pumps: Especially solar water pumps, where flow rate varies with sunlight.
HVAC Systems: To adjust airflow based on room temperature or occupancy.
Conveyor Belts: For speed adjustments in production lines.
Fans and Blowers: To regulate air pressure and reduce noise.
CNC Machinery: Where precision speed control is essential.
In agriculture, mining, and manufacturing sectors, a reliable variable frequency drive manufacturer like USFULL can deliver VFDs that meet harsh environmental requirements while maintaining top performance.
A Variable Frequency Drive is more than just a speed control device — it’s a solution for energy savings, equipment longevity, and operational control. Whether you’re managing a solar pumping system or automating a factory, choosing the right VFD supplier makes all the difference.