When your power system fails due to the wrong circuit breaker, it can cause fires, equipment damage, or even personal injury. A poor choice leads to safety risks, downtime, and financial loss. This guide helps you choose the right circuit breaker to protect your business, employees, and assets.
There are several types of circuit breakers based on voltage, interruption method, and installation. Choosing the right one involves understanding your environment, application, and safety requirements. Learn how to select the ideal DC or AC breaker for solar, residential, or industrial use.
Still unsure which breaker is right for your system? Keep reading to explore deeper insights.
Why is a Circuit Breaker Necessary?
A circuit breaker is the first line of defense in any electrical system. Its primary job is to detect and interrupt faults—like short circuits or overloads—before they lead to serious consequences. For example, an unprotected solar pump system could experience a current surge that damages expensive equipment or even starts a fire.
Whether you’re sourcing from a circuit breaker manufacturer in China or anywhere else, the need for reliable protection remains the same. Especially for DC applications such as solar, DC breakers must cut off dangerous surges instantly to prevent equipment failure or safety hazards. Without proper circuit breakers, you risk downtime, liability, and long-term damage.
What Features are Considered When Manufacturing Circuit Breakers?
Leading circuit breaker suppliers, especially in industrial manufacturing hubs like China, focus on key features that guarantee safety, efficiency, and reliability:
Voltage and Current Ratings: Whether it’s a breaker circuit for 230V residential power or a DC circuit breaker for solar arrays, matching specs is critical.
Trip Mechanism: Mechanical and thermal trip curves are calibrated based on ambient temperatures and system loads.
Environmental Suitability: Breaker DC models used in outdoor solar applications must withstand humidity, UV, and high temperatures.
Certifications: Reputable circuit breaker manufacturers provide CE, IEC, or TUV compliance, which is essential for export or installation approvals.
Maintenance Profile: Molded-case DC breakers are often preferred for their sealed design, requiring minimal upkeep.
As a trusted Circuit Breaker manufacturer in China, USFULL emphasizes advanced arc extinction techniques and compact designs to improve both safety and installability.
Classification of Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers are categorized based on several criteria: voltage level, interruption mechanism, and installation environment. Here’s how each type functions:
1. By Voltage Level
High-voltage Circuit Breakers: Used above 72kV, often for transmission systems. They utilize SF6 gas or vacuum for arc extinction.
Medium-voltage Breakers: Rated between 1kV and 72kV. Found in substations or industrial settings.
Low-voltage Breakers: Below 1kV, ideal for residential, commercial, or small-scale industrial use. Includes Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCB) and Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCB).
2. By Interruption Method
Air Circuit Breakers (ACB): Use air to extinguish the arc, typically in low-voltage systems.
Oil Circuit Breakers (OCB): Traditional and used in medium-voltage applications; now less common due to maintenance issues.
Vacuum Circuit Breakers: Ideal for indoor medium-voltage systems; efficient arc quenching.
SF6 Circuit Breakers: Used in high-voltage systems; excellent insulation but requires monitoring due to greenhouse gas concerns.
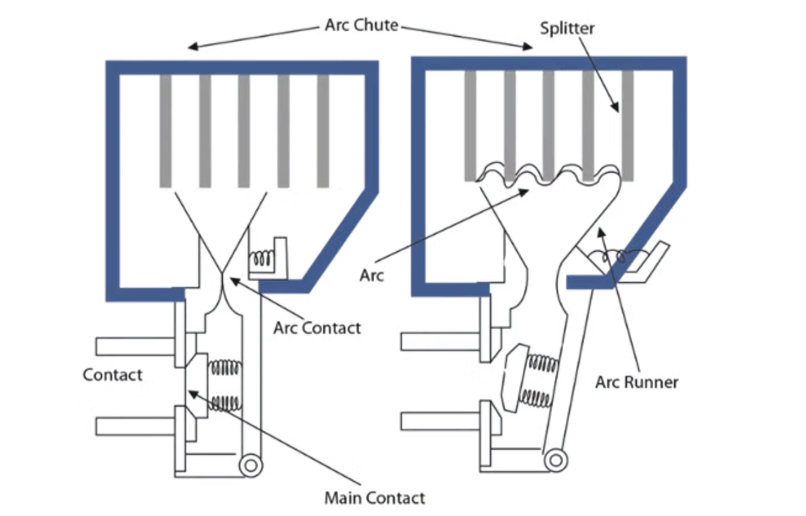
3. By Installation Location
Indoor Breakers: Enclosed systems typically found in control rooms or distribution panels.
Outdoor Breakers: Rugged enclosures designed to withstand rain, UV, and dust; used in substations and solar farms.
In solar applications, especially in pump control or off-grid systems, Solar DC Circuit Breakers are a must. These DC circuit breaker types prevent backflow currents and protect batteries and inverters.
Identifying the Right Circuit Breaker
Choosing the right breaker circuit for your system involves analyzing technical and environmental factors:
Voltage & Current Ratings: Always select a breaker DC rated for 120% of your maximum expected current. Underrated breakers risk frequent tripping or fire hazards.
Trip Curve Selection: For motor loads, use a delayed-curve breaker. For sensitive electronics, choose a fast-acting trip model.
Interrupting Capacity: Always ensure the breaker can safely interrupt the maximum potential fault current without damage.
Environment Conditions: In humid or corrosive conditions, use specially treated DC breakers with anti-fungal and anti-rust protection. For high-altitude installations, derating may be necessary.
System Type (AC or DC): AC breakers may not work correctly in DC systems. Always use DC circuit breaker models for solar setups, as they are designed to handle continuous DC current without arcing.
Certifications & Quality: Partner with a trusted circuit breaker supplier or circuit breaker manufacturer in China that offers testing reports, ISO certifications, and proven track records.
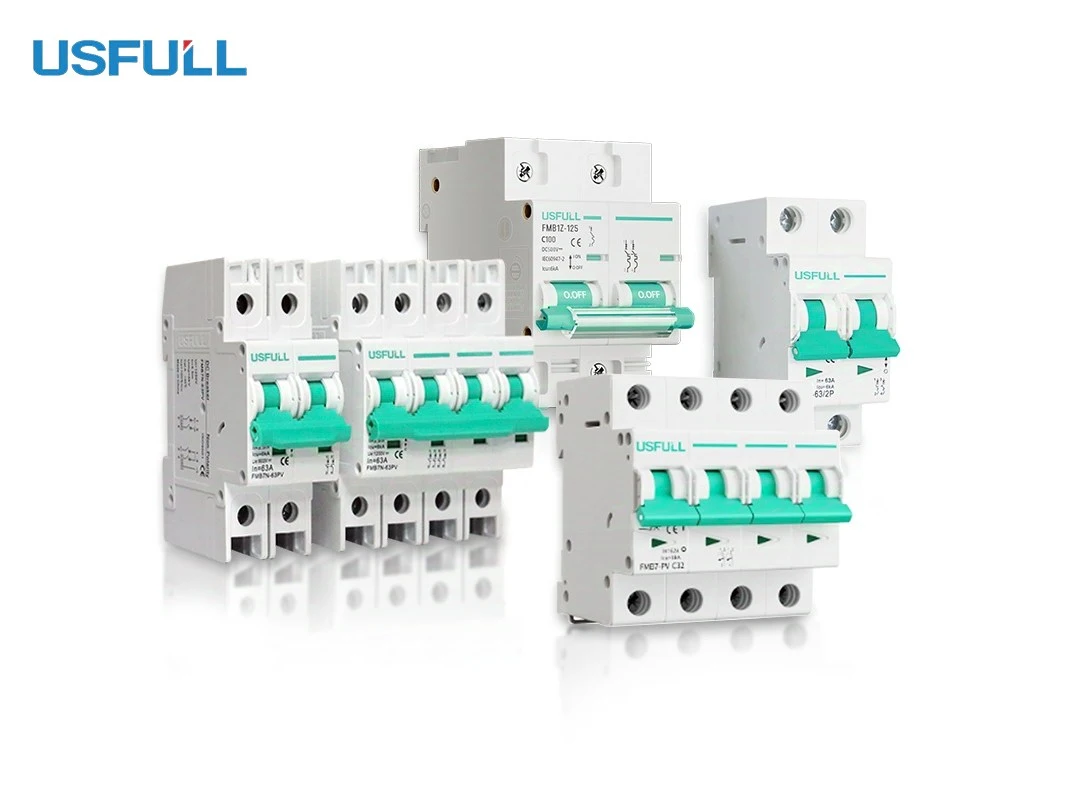

The right circuit breaker isn’t just a part—it’s a safeguard. For solar applications, especially where breaker DC technology is critical, the risks of using the wrong product are too high. A reliable Solar DC Circuit Breaker can protect your assets, your workforce, and your reputation.
Looking for a trusted DC breaker supplier? USFULL offers certified, high-quality DC circuit breakers with customizable options, fast delivery, and full technical support. As a leading Circuit Breaker manufacturer in China, we help businesses worldwide build safer, more reliable electrical systems.